In the realm of technology and creativity, the convergence of art and science often leads to groundbreaking innovations. One such innovation that has been making waves recently is the fusion of generative artificial intelligence (AI) with the world of 3D modeling and 3D printing. This amalgamation, often referred to as “Sculpting with Data,” is revolutionizing the way we approach design, manufacturing, and creativity in general.
The Art of 3D Modelling
Before we delve into how generative AI is changing the game, let’s first understand the basics. 3D modeling is the process of creating three-dimensional digital representations of objects, environments, or characters. These models serve as the blueprint for various industries, including architecture, gaming, healthcare, and manufacturing. Traditionally, 3D modeling required skilled artists and designers to meticulously craft these models, often through labor-intensive manual processes.
Generative AI: The Creative Catalyst
Generative AI, on the other hand, is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating algorithms and models capable of generating new data, content, or designs autonomously. These algorithms can learn from existing data and patterns, allowing them to produce novel and sometimes highly creative outputs.
The integration of generative AI into 3D modeling and printing has been nothing short of transformative. Here’s how it’s making an impact:
Automated Design Generation:
Generative AI algorithms can create 3D designs based on defined parameters and objectives. This means that designers can input their requirements, and AI can quickly generate a range of design options, saving time and effort.Complexity Beyond Human Capacity:
AI can produce intricate designs and patterns that would be exceedingly difficult, if not impossible, for humans to create manually. This is particularly beneficial in industries where precision and complexity are essential, such as aerospace and biomedical engineering.Customization at Scale:
3D printing is known for its ability to create customized products. Generative AI takes this to the next level by enabling mass customization. Each item produced can be unique, tailored to individual preferences or needs, without significantly increasing production time or costs.Optimized Material Usage:
AI-driven designs can be optimized for material usage, reducing waste in 3D printing processes. This not only benefits the environment but also improves cost-efficiency.Faster Prototyping and Iteration:
Design iterations and prototypes can be generated rapidly, accelerating the product development cycle. This is invaluable in industries where speed to market is a critical factor.Innovation and Exploration:
Generative AI encourages experimentation and innovation. Designers and engineers can explore unconventional shapes, structures, and materials, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.Artistic Expression:
Beyond the practical applications, generative AI in 3D modeling opens up new avenues for artistic expression. Artists can collaborate with AI to create unique sculptures, installations, and interactive art pieces.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the impact of generative AI on 3D modeling and printing is undeniably positive, it’s not without its challenges. These include concerns about intellectual property, data privacy, and the potential for job displacement. Striking a balance between human creativity and AI assistance is a critical consideration for the future.
Quality Assurance:
Ensuring that AI-generated 3D models meet quality standards is a multifaceted challenge. There may be issues with geometry, topology, or other aspects of the model that require human intervention for correction. While AI can automate much of the modeling process, there can still be issues with geometry, topology, texture mapping, or even artistic aspects of the model that require human intervention. Quality assurance teams need to develop processes and tools to identify and rectify these issues efficiently, which can be particularly challenging when dealing with large-scale or complex models.Data Quality:
Generative AI heavily relies on the quality and diversity of training data. If the data used for training is biased or incomplete, it can lead to the generation of flawed or inaccurate 3D models. Biased or incomplete training data can lead to AI models generating flawed or inaccurate 3D models. Addressing this challenge involves careful curation of training datasets, data augmentation techniques, and ongoing monitoring to detect and correct biases or data quality issues that may arise during the training process.Interoperability:
Compatibility between AI-generated 3D models and existing software and hardware systems can be a hurdle. Ensuring that models can be easily integrated into existing workflows is essential. Ensuring that AI-generated 3D models seamlessly integrate with existing software and hardware systems can be a significant hurdle. Compatibility issues may arise when attempting to use AI-generated models in various applications, such as CAD software, virtual reality environments, or game engines. Solving this challenge requires developing standardized formats and robust conversion tools to bridge the gap between AI-generated content and existing workflows.Complexity and Scalability:
Generating intricate 3D models, especially for large-scale applications, can be computationally intensive and time-consuming. Balancing complexity with efficiency is a challenge. Striking a balance between model complexity and computational efficiency is crucial. This may involve optimizing algorithms, utilizing distributed computing resources, or exploring novel techniques to expedite the generation process without compromising quality.Ethical Concerns:
There are ethical considerations related to the use of generative AI for 3D modeling, including questions about intellectual property, copyright, and the potential for AI to replace human designers and artists. Questions about intellectual property and copyright arise when AI generates content that resembles existing designs. Moreover, there are concerns about AI potentially replacing human designers and artists, leading to job displacement. Addressing these concerns necessitates the development of clear guidelines for intellectual property in AI-generated content and fostering collaboration between AI and human creators.
The Future of “Sculpting with Data”
- As generative AI continues to evolve and become more accessible, we can expect even greater innovations in 3D modeling and printing. The boundaries of what we can create will expand, and the lines between human and machine creativity will blur.
- Generative AI’s role in healthcare will continue to expand. We can anticipate AI-driven 3D modeling contributing to breakthroughs in organ transplantation through the creation of highly personalized and functional organ implants.
- The concept of digital twins, where physical objects or systems have a digital counterpart, will become more prevalent. Generative AI will enable the creation of highly accurate digital twins for products, infrastructure, and even entire cities.
- AI-generated art, music, and literature will become an integral part of our cultural landscape. AI algorithms will collaborate with human artists, creating innovative and thought-provoking works that challenge our notions of creativity and authorship. Art forms we can’t even imagine today will emerge.
3D Printing and the Fourth Industrial Revolution
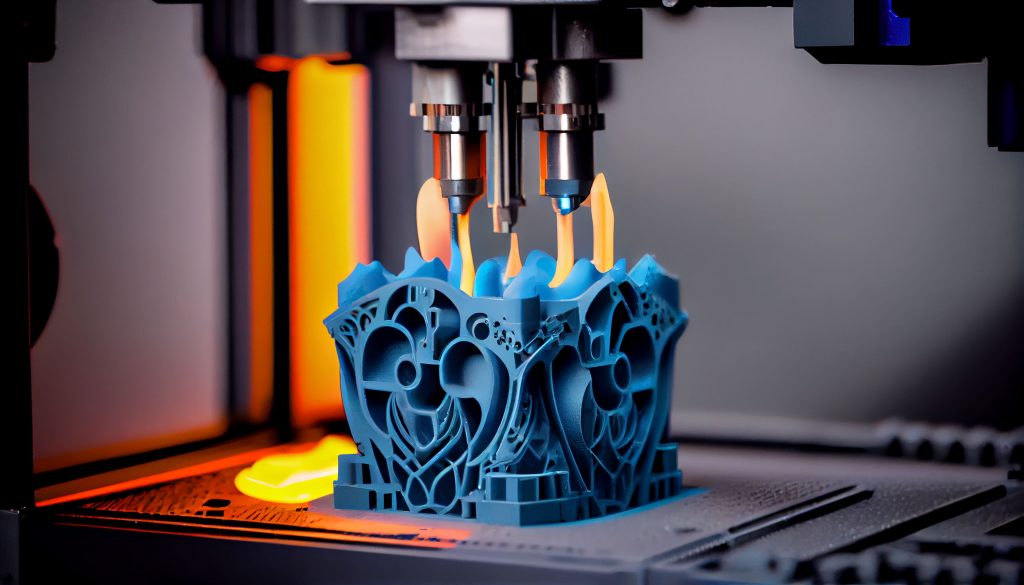

Generative AI’s role in 3D modeling is closely tied to the broader concept of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). This revolution represents the fusion of digital, physical, and biological technologies, and it’s reshaping industries worldwide. 3D printing is a key driver of 4IR, and generative AI is accelerating its progress.
Mass Customization:
4IR emphasizes the shift from mass production to mass customization. Generative AI, with its ability to create unique designs quickly, aligns perfectly with this trend. Companies can produce personalized products at scale, meeting the individualized demands of consumers.Decentralized Manufacturing:
The combination of 3D printing and generative AI enables decentralized manufacturing. Instead of centralized factories producing and distributing goods, local 3D printers can manufacture products on demand. This reduces transportation costs, carbon footprint, and the need for large inventories.Supply Chain Resilience:
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains. Generative AI and 3D printing offer the flexibility to adapt quickly to disruptions. When traditional supply chains falter, localized 3D printing can step in to produce essential items.
Industries Transforming Through Sculpting with Data
The impact of generative AI in 3D modeling and printing is pervasive, affecting a wide range of industries:
Healthcare:
Customized prosthetics, implants, and medical instruments are now possible through generative design. Surgeons can even use 3D models for pre-surgical planning. Generative AI accelerates drug discovery by modeling complex molecular structures and predicting potential drug candidates. Radiologists leverage generative AI to enhance the accuracy of medical imaging interpretation.Aerospace:
Lightweight, aerodynamic components and structures are designed with precision, improving fuel efficiency and safety in the aviation industry. Generative AI plays a pivotal role in developing autonomous flight systems. These systems enable aircraft to make split-second decisions based on real-time data, enhancing safety and opening the door to autonomous passenger and cargo flights. The precision and innovation driven by generative AI are instrumental in designing spacecraft for ambitious space exploration missions.Architecture and Construction:
Architects and engineers can create complex and sustainable building designs that were previously too intricate to build. Generative AI contributes to the development of smart cities with advanced infrastructure, intelligent traffic management, and energy-efficient buildings. These cities prioritize sustainability, convenience, and quality of life for residents. Architects and engineers use generative AI to analyze and mitigate the environmental impact of construction projects.Automotive:
Car manufacturers use generative design to reduce vehicle weight while maintaining safety standards. Generative AI contributes to the development of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). These systems include features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and automated emergency braking, enhancing road safety and reducing accidents. Generative AI enables the creation of personalized vehicle interiors. Car owners can choose from a wide range of interior layouts, materials, and infotainment options, resulting in unique driving experiences tailored to individual preferences.
Some notable companies that are actively leveraging Generative AI and 3D modeling to transform their industries:
Autodesk:
Autodesk is a leading software company that offers a range of design and engineering software solutions. Their generative design tools empower engineers and designers to explore thousands of design options for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and architecture.
GeekyAnts:
GeekyAnts offers a range of services related to software development, including web and mobile app development, UI/UX design, and consulting also incorporates AI-driven 3D modeling tools to create highly realistic environments and characters for immersive experiences.
Siemens:
Siemens uses generative design and AI-powered simulations to optimize product design and manufacturing processes. Their software solutions are particularly influential in the automotive and industrial machinery sectors.
SpaceX:
SpaceX, Elon Musk’s aerospace company, utilizes advanced 3D modeling and simulation software to design and test rocket components and spacecraft. Generative design aids in creating innovative and efficient space technologies.
The Future Beyond Static Models
While much of the discussion has revolved around static 3D models, the impact of generative AI extends beyond stationary objects:
Dynamic 3D Printing:
Advancements in generative AI can enable dynamic and adaptive 3D printing. Imagine a vehicle with tires that adjust their treads based on road conditions or shoes that adapt their soles to the terrain. Generative AI-powered 3D printing can revolutionize infrastructure construction. Imagine bridges and buildings that adapt to changing environmental conditions. Smart infrastructure could withstand earthquakes, monitor traffic in real-time, and even repair themselves when needed.Bioprinting:
Generative AI plays a role in Bioprinting, where living tissues and organs are 3D printed. The ability to generate complex organic structures is a game-changer for regenerative medicine. Generative AI in bioprinting can facilitate the production of 3D-printed tissue models for drug testing. These models simulate human organs and tissues, reducing the need for animal testing and accelerating drug development.Augmented and Virtual Reality:
The line between physical and virtual worlds blurs as generative AI creates immersive 3D environments for augmented and virtual reality experiences. Generative AI-driven virtual reality will redefine tourism. Travelers can visit exotic destinations from the comfort of their homes, experiencing immersive cultural and natural wonders in unprecedented ways.
Ethical and Creative Considerations
As generative AI becomes more integral to 3D modeling and printing, ethical considerations arise. It’s essential to strike a balance between AI assistance and human creativity. Additionally, issues surrounding data privacy, intellectual property, and AI-generated art’s attribution must be addressed.
In recent years, pioneers in the field of generative AI and digital transformation have been at the forefront of innovative solutions that have reshaped the landscape of 3D modeling and printing. Their work has demonstrated the incredible potential of harnessing data-driven creativity to revolutionize industries and push the boundaries of what’s achievable in the world of design and manufacturing. In the field of generative AI and digital transformation, leading companies such as GeekyAnts have made significant contributions.
Crafting Tomorrow: The Artistic Potential and Ethical Horizons of Generative AI in 3D Modeling and Printing
In conclusion, “Sculpting with Data: Generative AI’s Impact on 3D Modeling and Printing” represents a remarkable journey at the intersection of human creativity and technological advancement. This fusion of generative AI with 3D modeling and printing is more than just a trend; it’s a paradigm shift with profound implications across industries and creative endeavors.
In the grand tapestry of technology and artistry, “Sculpting with Data” is a testament to what humanity can achieve when we leverage technology to amplify our creativity. It’s a reminder that, as we continue to explore the boundless possibilities of generative AI in 3D modeling and printing, we are not merely sculpting objects; we are sculpting a future where imagination knows no limits, where art and innovation harmonize, and where human potential soars to new heights.
Discover how Generative AI is revolutionizing app interfaces in our blog post ‘Next-Level UI/UX: Enhancing App Interfaces with Generative AI,‘ where we explore the innovative techniques and tools shaping the future of user experience design.